Difference Between UMA and NUMA (with Comparison Chart) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › non uniform memory access › Difference Between UMA and NUMA (with Comparison Chart) |
Difference Between UMA and NUMA (with Comparison Chart)
|
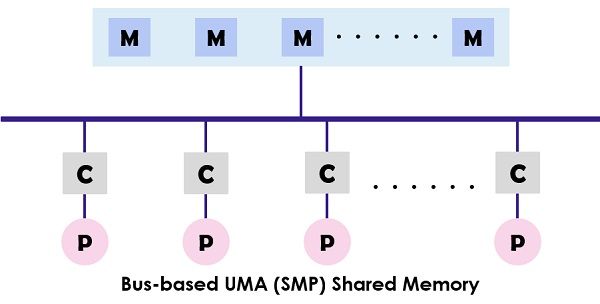
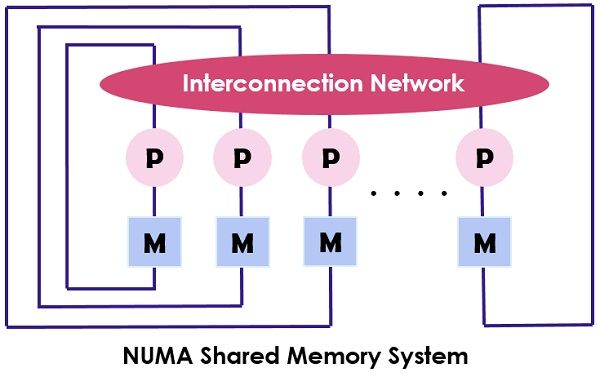
The bandwidth utilised in the UMA to the memory is restricted as it uses single memory controller. The primary motive of the advent of NUMA machines is to enhance the available bandwidth to the memory by using multiple memory controllers. Content: UMA Vs NUMA Comparison Chart Definition Key Differences Conclusion Comparison ChartBasis for comparisonUMANUMA BasicUses a single memory controllerMultiple memory controller Type of buses usedSingle, multiple and crossbar.Tree and hierarchical Memory accessing timeEqualChanges according to the distance of microprocessor. Suitable forGeneral purpose and time-sharing applicationsReal-time and time-critical applications SpeedSlowerFaster BandwidthLimitedMore than UMA. Definition of UMA UMA (Uniform Memory Access) system is a shared memory architecture for the multiprocessors. In this model, a single memory is used and accessed by all the processors present the multiprocessor system with the help of the interconnection network. Each processor has equal memory accessing time (latency) and access speed. It can employ either of the single bus, multiple bus or crossbar switch. As it provides balanced shared memory access, it is also known as SMP (Symmetric multiprocessor) systems. The typical design of the SMP is shown above where each processor is first connected to the cache then the cache is linked to the bus. At last the bus is connected to the memory. This UMA architecture reduces the contention for the bus through fetching the instructions directly from the individual isolated cache. It also provides an equal聽probability for reading and writing to each processor. The typical examples of the UMA model are Sun Starfire servers, Compaq alpha server and HP v series. Definition of NUMANUMA (Non-uniform Memory Access) is also a multiprocessor model in which each processor connected with the dedicated memory. However, these small parts of the memory combine to make a single address space. The main point to ponder here is that unlike UMA, the access time of the memory relies on the distance where the processor is placed which means varying memory access time. It allows access to any of the memory location by using the physical address. As mentioned above the NUMA architecture is intended to increase the available bandwidth to the memory and for which it uses multiple memory controllers. It combines numerous machine cores into “nodes” where each core has a memory controller. To access the local memory in a NUMA machine the core retrieves the memory managed by the memory controller by its node. While to access the remote memory which is handled by the other memory controller, the core sends the memory request through the interconnection links. The NUMA architecture uses the tree and hierarchical bus networks to interconnect the memory blocks and the processors. BBN, TC-2000, SGI Origin 3000, Cray are the some of the examples of the NUMA architecture. Key Differences Between UMA and NUMA The UMA (shared memory) model uses one or two memory controllers. As against, NUMA can have multiple memory controllers to access the memory. Single, multiple and crossbar busses are used in UMA architecture. Conversely, NUMA uses hierarchical, and tree type of busses and network connection. In UMA the memory accessing time for each processor is the same while in NUMA the memory accessing time changes as the distance of memory from the processor changes. General purpose and time-sharing applications are suitable for the UMA machines. In contrast, the appropriate application for NUMA is real-time and time-critical centric. The UMA based parallel systems work slower than the NUMA systems. When it comes to bandwidth UMA, have limited bandwidth. On the contrary, NUMA has bandwidth more than UMA. ConclusionThe UMA architecture provides the same overall latency to the processors accessing the memory. This is not very useful when the local memory is accessed because the latency would be uniform. On the other hand, in NUMA each processor had its dedicated memory which eliminates the latency when the local memory is accessed. The latency changes as the distance between the processor and memory changes (i.e., Non-uniform). However, NUMA has improved the performance as compared to UMA architecture. Related Differences: Difference Between Multiprocessor and Multicomputer Difference Between Symmetric and Asymmetric Multiprocessing Difference Between Jitter and Latency Difference Between Loosely Coupled and Tightly Coupled Multiprocessor System Difference Between Multiprocessing and Multithreading |
【本文地址】
 Multiprocessors can be divided into three shared-memory model categories- UMA (Uniform Memory Access), NUMA (Non-uniform Memory Access) and COMA (Cache-only Memory Access). The models are differentiated based on how the memory and hardware resources are distributed. In the UMA model, the physical memory is evenly shared among the processors which also have equal latency for every memory word while NUMA provides variable accessing time for the processors to access the memory.
Multiprocessors can be divided into three shared-memory model categories- UMA (Uniform Memory Access), NUMA (Non-uniform Memory Access) and COMA (Cache-only Memory Access). The models are differentiated based on how the memory and hardware resources are distributed. In the UMA model, the physical memory is evenly shared among the processors which also have equal latency for every memory word while NUMA provides variable accessing time for the processors to access the memory.